How to Read and Understand Legislative Bills: A Beginner's Guide
Learn how to easily read and understand legislative bills with a simple three-step method and helpful tools.

Reading legislative bills doesn't have to be overwhelming. Here's a simple way to break them down:
- Understand the Purpose: Start with the title and first section to grasp the bill's intent.
- Spot Changes: Look for underscored text (additions) and ~strikethroughs~ (deletions) to identify updates to existing laws.
- Assess the Impact: Focus on effective dates and specific outcomes to see how the bill affects you or your community.
Key Features of a Bill
- Title: Summarizes the bill's subject.
- Sections: Details legal changes and provisions.
- Effective Date: Specifies when the law takes effect.
- Ramseyer Provisions: Highlights changes in the text.
Tools to Help
- Cicada.guide: AI-powered analysis with color-coded summaries.
- Congress.gov: Tracks federal legislation.
- OpenStates.org: Focuses on state-level bills.
By following these steps and using the right tools, you can confidently understand any bill and engage in the legislative process.
How to Read and Understand Legislative Bills: Examples From Nebraska
Parts of a Legislative Bill
Understanding the structure of a legislative bill can make these documents less intimidating. Every bill follows a standardized format designed for clarity and legal consistency. This structure lays the groundwork for analyzing bills effectively, as detailed in the next section.
Main Parts of Every Bill
Legislative bills typically include several key components:
| Component | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Bill Number | Serves as a tracking identifier | |
| Title | Summarizes the subject broadly | "A Bill For An Act Relating To Education" |
| Purpose Section | Explains the intent behind the legislation | States why the law is needed |
| Body Sections | Outlines specific provisions | Details legal changes and requirements |
| Effective Date | Specifies when the law takes effect | "This Act shall take effect on July 1, 2025" |
Ramseyer Provision
Bills often include Ramseyer provisions to highlight changes. These changes are shown through underscored additions and ~[bracketed strikethroughs]~.
"The title must encompass the bill's entire subject matter" - Hawaii Legislative Reference Bureau
How Bills Are Organized
Bills are written in a hierarchical format to break down complex legal details into smaller, more digestible sections. The structure typically includes:
- SECTIONS (numbers)
- Subsections (lowercase letters)
- Paragraphs (numbers)
- Subparagraphs (capital letters)
- Clauses (Roman numerals)
Certain sections often receive extra attention, such as severability clauses, appropriations, emergency clauses, and sunset provisions. These organizational elements are essential for applying the analysis techniques outlined in the upcoming 3-step process.
3 Steps to Read Any Bill
To understand a bill effectively, follow this three-step approach:
Step 1: Understand the Bill's Purpose
Begin by reviewing the bill's title and first section. These parts outline the bill's intent and objectives. Titles often start with phrases like "A Bill For An Act Relating To..." and provide a broad overview. The first section, or "Statement of Policy", typically contains the core purpose.
| Component | Location | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose Statement | Section 1 | Explains the legislative intent |
| Definitions | Early sections | Specifies legally binding terms |
| Scope | Title and preamble | Highlights jurisdictional coverage |
"Every law enacted must be introduced in the Legislature in the form of a bill...the title must encompass the entire subject matter." - Hawaii State Constitution
Step 2: Identify Changes to Existing Laws
The Ramseyer provisions are your guide here. Look for formatting marks that highlight changes: underscored text for additions and ~strikethroughs~ for deletions.
Key indicators to focus on include:
- Verbs like "establish", "amend", or "repeal", which signal major updates
- Changes to definitions that alter the scope or application of the law
- New rules, restrictions, or requirements being introduced
Step 3: Assess the Impact on You
Finally, connect the bill's content to its practical effects. This step ensures you understand how the changes might influence you or your community. Pay attention to these critical aspects:
- Effective dates (usually in the final section) and the groups or individuals subject to the law
- Sections that outline specific outcomes, such as new obligations, penalties, rights, or funding allocations
Ask yourself: When do these changes take effect? What actions are required? Are there penalties for non-compliance? Who might qualify for exemptions?
Tools to Help Read Bills
These resources work alongside the three-step analysis method to make reading and understanding bills easier:
Cicada.guide: AI-Powered Bill Analysis
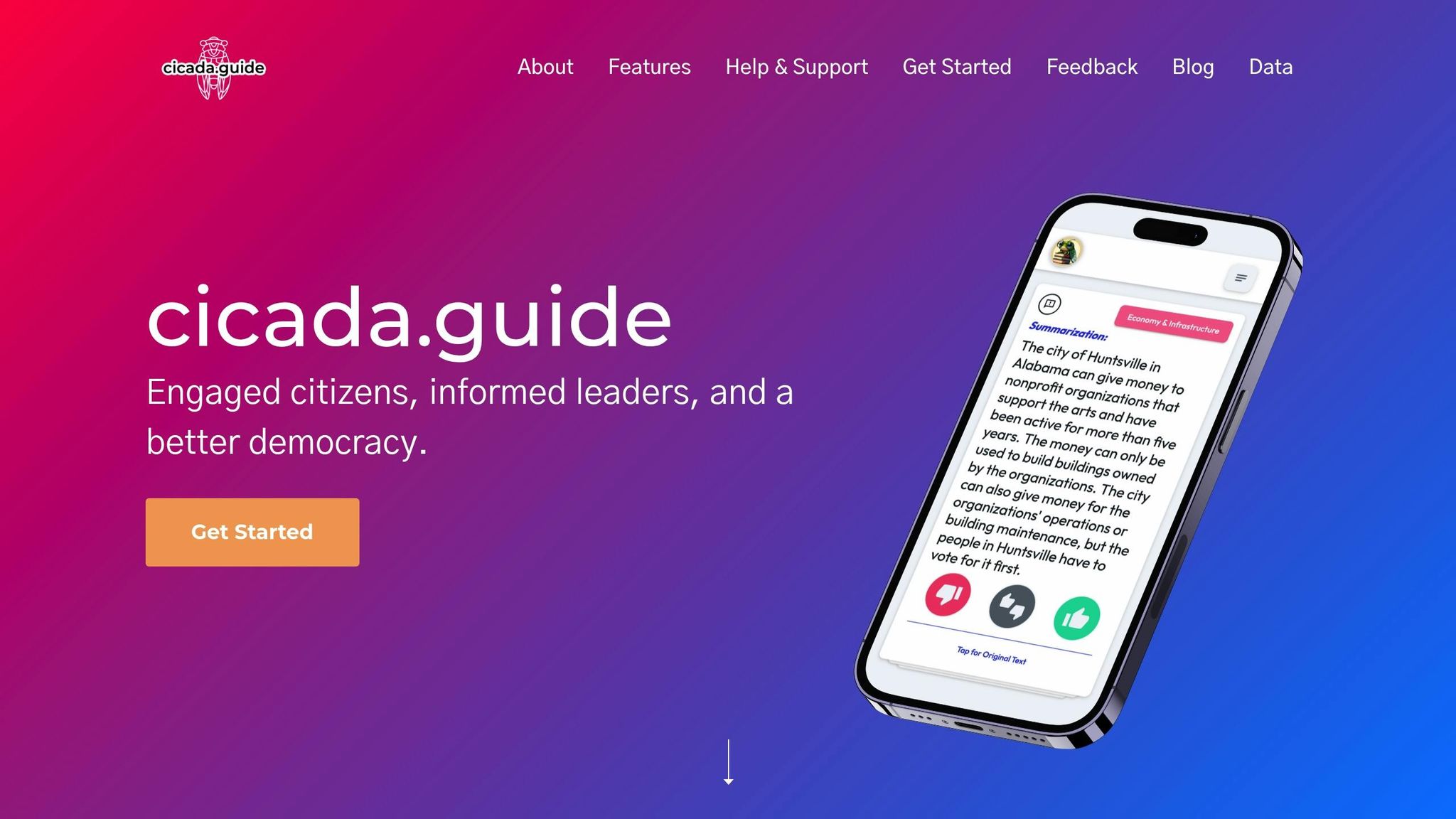
Cicada.guide uses artificial intelligence to break down legislative text. Here’s what it offers:
- Automated analysis that pinpoints key parts of a bill
- Color-coded tags to highlight impacts like "New Appropriation" or "Criminal Penalty"
- Simplified summaries of complex legal terms
- Version comparison tools to spot changes between bill drafts
Where to Find Legal Terms
Understanding legislative terminology is easier with reliable sources. Here are two trusted options:
| Resource | Features | Content Coverage |
|---|---|---|
| California Legislative Glossary | Over 200 defined terms | Covers procedural and legal definitions |
| Delaware General Assembly Glossary | Focus on procedural terms | Explains legislative process terminology |
Bill Tracking Websites
For real-time updates on legislation, these platforms are excellent:
Congress.gov
- The official source for federal legislation
- Includes a complete history of amendments
- Free and open to the public
- Tracks over 76,000 active bills across U.S. jurisdictions
- Offers real-time updates
OpenStates.org
- Focuses on state-level bills with searchable databases
Conclusion: Using Your Bill Reading Skills
Key Takeaways
By following the steps and tools shared earlier, you can transform bill reading into a powerful way to engage with legislators and participate in civic matters. The skills outlined in Steps 1-3 can make your efforts with lawmakers much more effective.
Here are some essential tips for analyzing bills:
- Track bill numbers: Pay attention to prefixes like HB (House Bill) or SB (Senate Bill).
- Understand titles: Titles often begin with "Relating To…" and can give you a quick summary of the bill's focus.
- Read markup symbols carefully: Underscores and strikethroughs highlight changes in the bill.
- Check effective dates: These are usually found in the final sections and are crucial for understanding when the bill takes effect.
Ways to Get Involved
The Nebraska Legislature glossary suggests several ways to make your voice count:
- Committee Testimony: When testifying, refer directly to specific sections of the bill. This makes your arguments more precise and impactful.
- Digital Tools: Stay updated by using resources like OpenStates.org, which offers a visual tracker for amendments.
-
Stay Active Year-Round: Keep your engagement consistent by:
- Reviewing pre-filed bills during off-session periods.
- Practicing with past legislation to understand outcomes.
- Attending free educational events like the NCSL Citizen Legislative Academy.
FAQs
How to read a legislative bill?
Use the three-step method outlined earlier while paying attention to these key structural components:
Start by checking the bill's current stage using the tracking tools mentioned in Step 3. Then, break down the bill systematically by focusing on these elements:
Title: The title usually starts with "A Bill For An Act Relating To..." and gives a general idea of the bill's subject.
Key Sections to Review
| Section | What It Provides |
|---|---|
| Legislative Counsel's Digest | A plain-language summary of the bill's effects |
| Statutory Reference | Citations to existing laws being amended or referenced |
Other Important Areas to Examine
- Look for the Definitions section (typically near the beginning) to understand technical terms.
- Pay attention to formatting symbols (like additions or deletions) to track changes, as explained earlier.
Combine this structural breakdown with the three-step process (Purpose, Changes, Impact) to get a clear understanding of the bill. You can also use Cicada.guide's color-coding tools (discussed earlier) to speed up your review.




